I do not know who will ‘win’ GE2020, but I do know who will be held responsible for delivering the victory: The Silent Majority.
In Singapore, there’s no phrase more popular or more frequently abused. PAP MPs, when speaking to ST journalists, will emphasise ad nauseam the importance of listening to the Silent Majority. ST columnists, upon returning to their cubicles, will write lengthy columns speculating on the Silent Majority’s alleged sympathies.
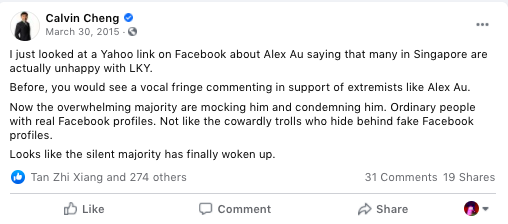
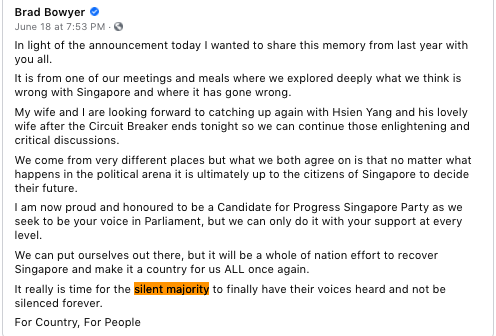
History, however, tells us a different story.
In Singapore, the first recorded use can be traced back to 1961. During a speech at the University of Malaya Student Union, Lee Kuan Yew (LKY) bashed the Communists for using ‘silent intimidation’ against their detractors. Since many were “cowed into silence by the fearful consequences which they dread will befall those who stand up to the Communists”, the majority (“who are quiet, not noisy”) ended up being the minority.
He then called upon the students to “take a stand” against the “left-wing adventurers” who want to establish a “Communist Malaya”.
Although the words “silent” and “majority” were never placed adjacent to one another, LKY’s message was quite clear: the silent majority, who opposed communism, had to make their voices heard, or else we would all be singing Lenin’s praises, at the behest of an outspoken communist minority.
This early-access version of the ‘silent majority’ was sometimes used by the PAP Old Guard. Minister S Rajaratnam, for example, expressed a similar sentiment in 1976: “A communist minority, I grant, can be far more noisy than the silent majority.”

It was mostly directed at the lack of—dare I say it—activism.
In 1971, an NUS student named Doreen D’cruz lamented the indifference of Singaporean Youth, who were ‘the silent majority without a social conscience’. At the YWCA/YMCA Youth meeting, ST reported on her rather proto-SJW complaint that Singaporean youth lacked not only political commitment but ‘any sort of commitment’.
Her views were echoed by—no kidding—the Singapore Law Society in 1977. When a mere 31 of its 500 members replied to its letters, the Society’s President was so enraged that it resulted in an ST editorial entitled The Silent Majority—which more or less harangued our nation’s lawyers for their bo-chup attitudes towards the building of a legal community.

These mentions were few and far between, but the term did enjoy a not-insignificant endorsement—from the ST editorial board itself. In a 1983 editorial entitled ‘The Straits Times says: Worse than Silent Majority’, our national broadsheet condemned the lack of civic participation amongst Singaporeans. It argued that Singapore’s “silent majority” of apathetic workers is bad, but nowhere as horrifying as the highly-educated liberal elite who can afford to chip in, but largely refuses to do so.
“In most societies, there is an articulate minority, Singapore cannot be the exception. Yet, the trouble is that national leaders and some more concerned citizens apart, we do not seem to have even an articulate minority,” the article lamented.
On the PAP front, there was much wailing and gnashing of teeth. PM Goh attributed his devastatingly incomplete victory to an excess of liberalism. However, the media were more interested in LKY’s views on the issue, which eventually proved to be more influential—at least in my opinion.
When interviewed by SPH reporters, LKY blamed his party’s “loss” on a failure to listen to the “silent majority of Chinese-educated Singaporeans”. The PAP had “neglected” the concerns of the Chinese-educated—Nantah graduates—who felt they were being “squeezed out of the mainstream”, and thus sided with the Teochew-fluent Low Thia Khiang.
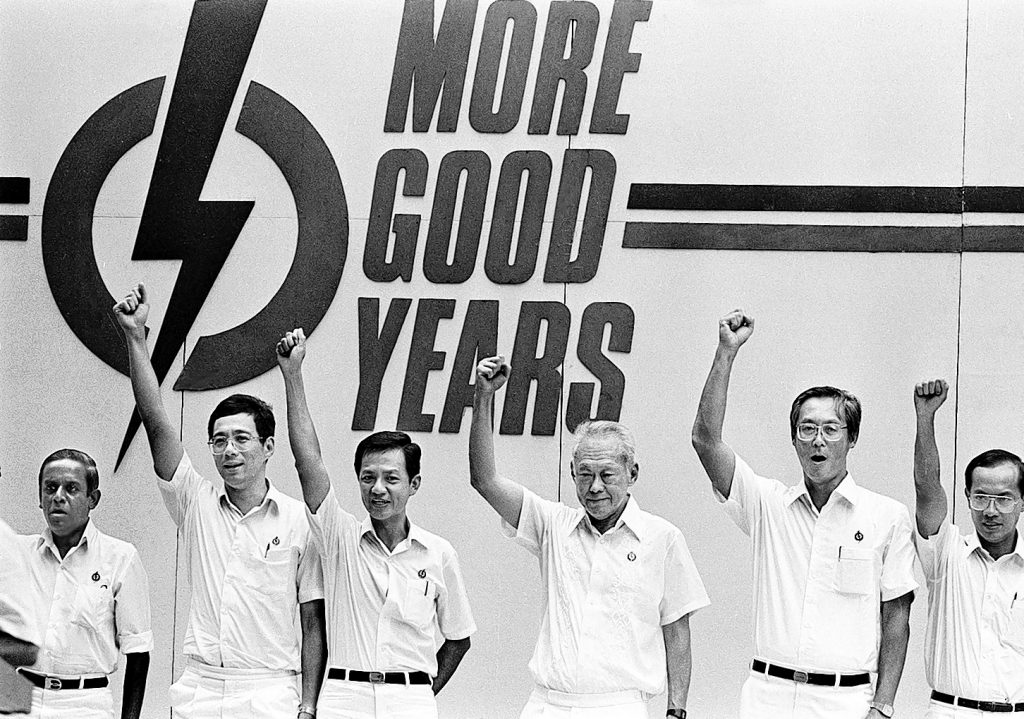

In a rare instance of PAP-on-PAP violence, Ah Gong even scolded his Ministers for their English-centric reading habits (ST rather than Lianhe Zaobao) and rather coldly suggested that Mr Goh must “draw his own lessons from the election”.
Regardless, his views on the Chinese silent majority would be reprinted in every newspaper, under slightly different headlines. One editorial said that Ministers had “lost touch” of “ground sentiments”, while another said of the Chinese-educated Silent Majority: “They voted opposition because they felt neglected by the government”.
Interestingly, however, LKY also emphasised that their grievance was “socio-political” rather than “economic”. What they wanted was not so much a more comfortable living, but their “fair place in the sun”.
As for the “western liberal types among the English-educated, their orientation was not towards political activism,” he added.
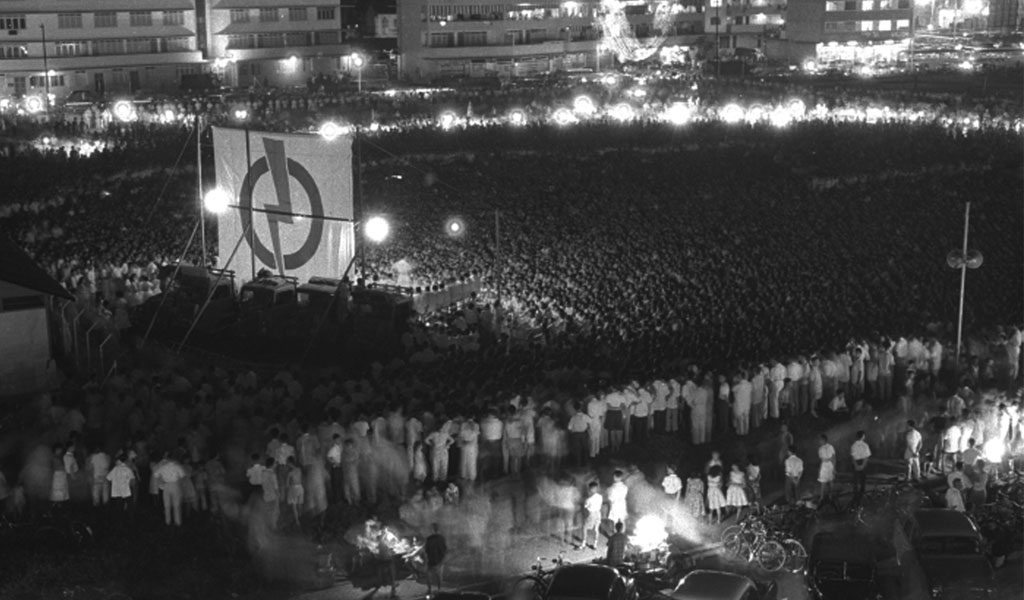

In any case, what really went down in 1991 is not important for this article. What’s really important was the influence of LKY’s thesis of the “Chinese-educated Silent Majority”, which had—I would argue—a profound impact on the way we now think about politics.
Although LKY mostly blamed his own Ministers for the 1991 election “debacle” rather than the “English-educated liberal types”, his message seems to have been garbled in its reception. Post-1991, it gradually acquired a distinct tone of partisanship and hostility—as if the articulate minority were somehow responsible for silencing the majority.
In 1992, for example, Parliamentary Secretary Ong Chit Chung, having taken LKY’s advice to heart, gave a speech about censorship which oscillated between defensiveness and accusation. The silent majority must have their due consideration, he said, and the government cannot be expected to “pamper the vocal minority”. “Liberals,” he warned, “should not exploit their position to propagate their views and open up society.”

This is quite a departure in tone from the 1980s, when ST was crying out for an articulate minority, however small, to take an interest in civil society. This rhetoric soon disappeared from view and was replaced by the tug-of-war we know so well. The relationship between a vocal minority/silent majority, once non-existent, had acquired the meaning of oppressor/oppressed, bully/victim, as if speech was a zero-sum game, and one opinion is always expressed at the expense of another.
In short, the Silent Majority had become a Silenced Majority.
However, the term continued to retain the us-versus-them mentality which it acquired in the 1990s.
Its most prominent adopters were those opposed to LGBTQ voices, who took up the ‘silent majority’ rhetoric against what it saw as an increasingly strident gay-rights movement. In 2009, The New Paper published a report entitled “‘Silent’ Majority Turns Up The Volume”. The article begins with a line which read: “They are the ‘Silent Majority’ who say gay sex is wrong”, and featured the views of one “Mr Martin Tan, 30”, who started a petition to “keep 377A” because “it was time for the majority to speak their mind”.

“What about ‘the plight of the silent majority’ who were in favour of en bloc?” the author complained. A delay in selling would delay the money’s arrival and who then would compensate him for the lost interest?

During its victory lap, ST once again dug up the ‘Silent Majority’ trope for ol’ times’ sake. Its longtime Opinion editor Ms. Chua Mui Hoong wrote a piece titled ‘Silent majority’s roar of support for PAP’. In this latest iteration, the silent majority took on a new meaning. It was no longer the apathetic, the Chinese-educated, or the socially conservative ‘silent majority’ of yesteryear, but a majority whose voices were ‘silent’ on the internet or social media.
Is this oft-repeated explanation correct?
According to ST’s own report dated Sep 13, 2015, the answer is ‘probably not’. The media monitoring house Meltwater Analytics trawled different social media channels to analyse the political leanings of—god help them—internet comments. They found that our ruling party had received the lion’s share of both criticism (14%) and praise (12%).
As it turns out, the silent majority is anything but silent—just not particularly interesting. The ‘Chinese’ part was probably dropped because you can’t say that in 2015.
Does the silent majority exist? Of course it does, but in the same way that the ‘average Singaporean’ exists, as a category so vague it’s completely meaningless.
Which begs the question: why are we so fond of the term?
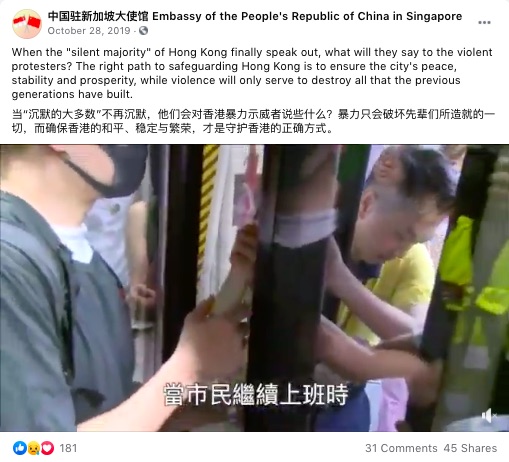
That’s why the term has been appropriated by those who wanted to keep 377A. It’s not very sympathetic to side with the large well-organised interest groups. Much better to recast yourself as the victims of vocal pro-LGBTQ minority or the ‘Gay Agenda’, whose influence is all-pervasive.
In doing so, the real injustice of unequal legal status is conflated with the imaginary injustice of having your worldview challenged. In other words, it’s not the LGBTQ community who suffers discrimination in matters of marriage or housing, but we—the Silent Majority—who are oppressed by queer voices in the public sphere.
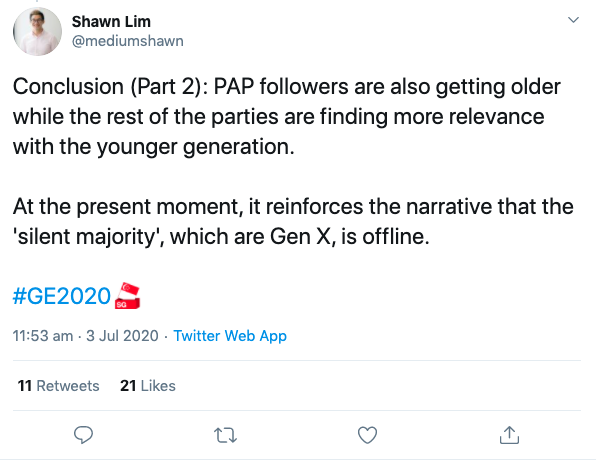
If you’re generous, it can be construed as an attempt to be ‘close’ to their constituents. If you’re cynical, it’s just so much virtue-signalling—like US senators talking about “Main Street instead of Wall Street” or “real, hard-working Americans”.
What was once an off-the-cuff remark by LKY has ballooned into an ever-expanding cliché which encompasses basically every imaginable demographic: Chinese, heartland, economic, socio-political, conservative, liberal, en bloc preference, educational status and so on. As a member of the vocal minority who dislikes motherhood statements, I say it’s time we confine this phrase to its rightful place in the trash can.
1. NLB microfilm: NL06895, NL09340, NL13993, NL 17490, NL33084, NL27085, NL28541,NL17497
2. President Ong Teng Cheong predicted the 1991 General Election results. In 1981, he gave a speech which contained the following statement: “The Chinese educated have often wondered if they are there only to be pushed around. why can’t they have the right to take part in policy decision-making? But they keep their grievances to themselves, and have become the neglected “silent majority”. Indeed their unhappiness is not the result of recent developments. They have probably felt this way for a long time. The PAP will take a serious look at this particular issue in greater depth. The feeling of dislocation of the society among the Chinese educated Singaporeans must be corrected at the earliest opportunity.” As far as I can tell, however, it did not have wide circulation.







